Featured
Influenza Vaccine Efficacy
New vaccines with improved clinical efficacy and effectiveness are. Efficacy vs Effectiveness Vaccine efficacy- reduction in disease incidence in a vaccinated group compared to an unvaccinated group under optimal conditions eg RCT Typically use objective outcomes- eg lab-confirmed influenza designed to maximize internal validity by randomization and allocation concealment.
Flu vaccines will not prevent COVID-19 but they will reduce the burden of flu illnesses hospitalizations and deaths on the health care system and conserve scarce medical resources for the care of people with.

Influenza vaccine efficacy. The estimated effectiveness of the vaccine may depend on a number of. This review highlights the current insights and future perspectives into host. The efficacy of LAIV against influenza viruses antigenically similar to the vaccine was 423 95 CI 216-578.
Too few cases of. Healthy adults who receive inactivated parenteral influenza vaccine rather than no vaccine probably experience less influenza from just over 2 to just under 1 moderate-certainty evidence. To establish how well influenza vaccines work each season influenza vaccine effectiveness is measured in observational studies.
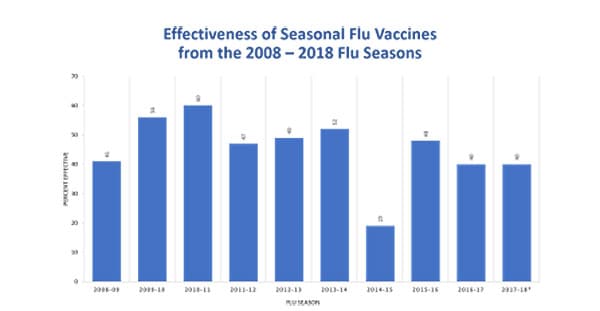
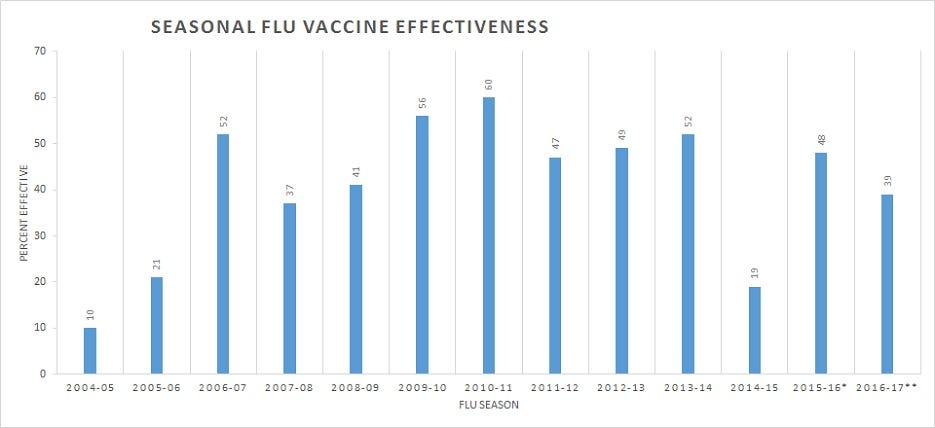
Median monovalent pandemic H1N1 vaccine effectiveness in five. Oral vaccination of mice with inactivated whole influenza vaccine induces systemic and mucosal immunity providing complete protection against homologous or heterologous challenge infections. In general influenza vaccine effectiveness has been found to vary between 30-60.
Six 35 of 17 analyses in nine studies showed significant protection against medically attended influenza in the outpatient or inpatient setting. Relative efficacy estimates indicated that the inactivated vaccine had outperformed the live attenuated vaccine by 60 95 CI 33 to 77 for protection against influenza A. There are many reasons to get an influenza flu vaccine each year.
CDC uses three networks to estimate vaccine effectiveness. Efficacy against AH3N2 viruses was 525 95 CI 321-672. By comparison the influenza vaccine efficacy for the 201718 season was 15 2.
Flu VE Network currently consists of five study sites across the United States that measure the flu vaccines effectiveness at preventing outpatient medical visits due. Influenza vaccine effectiveness Vaccine effectiveness is an estimate of the likelihood that a vaccine prevents influenza infection when used in everyday practice. Evidence for protection in adults aged 65 years or older is lacking.
We hypothesize that host genetics the hormonal milieu and gut microbiota contribute to host-related differences in influenza virus vaccine efficacy. Influenza vaccine provided clinically effective protection against influenza illness in HIV-1-infected patients. In baseline antibody-negative patients anti-H1 and anti-H3 antibody responses to the vaccination were significant in those patients with a CD4 count 200 cellsmuL compared with those with a CD4 count.
The vaccine must be changed each year in hopes of matching the ever-mutating viruses. Influenza vaccines can provide moderate protection against virologically confirmed influenza but such protection is greatly reduced or absent in some seasons. Vaccine effectiveness was variable for seasonal influenza.
Oral delivery of inactivated whole influenza virus vaccines has been recognized as an effective vaccination route. Growing evidences suggest that host factors including age biological sex pregnancy and immune history play important roles as modifiers of influenza virus vaccine efficacy. They also probably experience less ILI following vaccination but the degree of benefit when expressed in absolute terms varied across different settings.
Influenza leading to attendance at a general practice or hospitalisation than an unvaccinated person. Flu VE Network the Hospitalized Adult Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network HAIVEN and the New Vaccine Surveillance Network NVSN. This implies that on average a vaccinated person is 30-60 less likely to experience the outcome being measured eg.
In contrast in baseline antibody-positive patients good. Because of the on-going COVID-19 pandemic getting a flu vaccine during 2020-2021 will be more important than ever. Of course the weapon of choice in these debates are the meta analysis.
LAIVs consistently show highest efficacy in young children aged 6 months to 7 years. On average its been 40 effective meaning its prevented illness 40 of. The absolute vaccine efficacy for prevention of respiratory illness caused by vaccine-matched strains was 351 95 CI 179487 meaning the study did not meet its primary endpoint 70 efficacy.
Vaccine efficacy was not observed against antigenically similar B strains PubMed. Overall the evidence base for the efficacy and effectiveness of newer and enhanced influenza vaccines appears limited at present with a number of potentially relevant studies identified as ongoing. And thats been a challenge.
Popular Posts
How To Tell The Difference Between Lice And Dandruff
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps











Comments
Post a Comment